When the Internet launched back in 1989, people started sharing information in exciting new ways. Entire industries were launched, old ones were reworked, and the face of business communication changed forever. Fast forward 40 years and it’s still the same story, but on a much more epic scale. The Internet has single-handedly destroyed the traditional working world. Yet it’s also spawned entire industries ripe for disruption and innovation. Enter digital publishing.
Publishing has changed over time as new technologies continue to spur innovation. Today, turnkey solutions are infiltrating every industry imaginable and helping businesses gain an advantage over the competition. In fact, the digital publishing industry is expected to reach $68.81 billion in 2026 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.4%, according to the Digital Publishing Global Market Report 2022.
But digital publishing can mean different things to different people. And that can leave many of us confused. Don’t fret—we’re here to help you make sense of it all.
Digital publishing. What is it, exactly?
Let’s break it down first. “Digital” refers to electronic or computerized technology, any online media available on electronic devices, including laptops and pads. “Publishing” as defined by Merriam-Webster’s online dictionary, involves “bring[ing] printed works (like magazines, books, and catalogs) before the public usually for sale.” Put two and two together and digital publishing gets a whole lot easier to understand. It means using online technology to digitize written or print material and disseminate it through electronic devices.
The best digital publishers are experts at their craft, creating editorial, highly engaging content and distributing it online to:
- Increase the engagement rates
- Reach mobile, and global audiences
- Increase the conversion rates of the content
- Track performance with detailed analytics
- Increase reader retention and decrease subscriber churn rates
- And of course, save money by going from print to digital
To sum up, a digital publishing platform is a modern digital cloud-based service or software that enables publishers to efficiently produce, manage, release, monitor, analyze, and disseminate content on the Internet. These platforms offer a range of tools and functionalities that streamline the process of sharing various types of content, such as digital magazines, e-catalogs, digital brochures, articles, blogs, flipbooks, ebooks, guides, reports and more across the web.
Digital vs. Print Publishing: A Comprehensive Comparison
For business models rooted in tradition/print, transitioning to a digital format can disrupt production, marketing, and distribution processes. That’s good and bad news, so it’s important to know the opportunities and risks inherent to each medium. Let’s start with a comprehensive comparison table
| Digital Publishing | Print Publishing | |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Digital | |
| Distribution | Distributed through online platforms like websites, social media, digital publishing platforms and apps | Circulated via bookstores, newsstands, and libraries |
| Costs of Production | Content creation costs. Low Distribution costs | Initial content creation costs are similar; High production and distribution costs |
| Ease of Access | Instantly accessible on devices | Access depends on physical distribution networks |
| Impact on the Environment | Lower physical footprint due to virtual nature | Requires more resources for paper production and physical distribution, increasing environmental impact |
| Interactivity | Rich interactive features like multimedia, links, and engagement tools | Generally lacks interactive capabilities, offering a straightforward reading experience |
| Content Updates | Can be updated or corrected swiftly post-publication | Any changes require reprinting, making updates cumbersome |
| Cost | Can vary, with many digital options being cheaper or free due to different monetization strategies | Typically more costly due to physical production and distribution costs |
| Insights and Metrics | Detailed insights into user engagement and content performance are readily available | Does not offer direct means to measure reader engagement or preferences |
| Marketing Data | Facilitates direct data collection for refined marketing and personalization | Offers limited opportunities for direct data collection, hindering precise marketing efforts |
| Feedback | Enables immediate interaction and feedback through digital channels | Indirect feedback methods such as letters or sales figures, lacking immediacy |
The Advantages and Challenges of Print Publishing
Print publishing pros
1. Traditional publishers can enlist the help of agents - industrious fellows who fight hard to ensure you and your work get noticed. The best ones land book deals, negotiate contracts, and mentor authors to further their writing careers. In short, they’re pretty darn helpful.
2. Distribution can be fairly straightforward. Bookstores, libraries, and other brick-and-mortar outlets can house your content for potentially hundreds of customers to admire. And the best part? Technology isn’t required. That’s pretty great.
3. Text on paper is final. There’s no turning back and you can’t change or update anything once your content is published and in the hands of consumers.
Print publishing cons
1. Traditional print publishing requires paper and printing materials. Online publishing doesn’t. Naturally, print publishing is much more expensive than its digital counterpart.
2. Time isn’t always at your side. It can take an entire year for a book to ever see the light of day. Writing, editing, and printing can extend the wait even further. Print means a lot of patience!
3. Text on paper is final. There’s no turning back and you can’t change or update anything once your content is published and in the hands of consumers.
The Advantages and Challenges of Digital Publishing
Digital publishing pros
1. Digital publishing is incredibly accessible. Practically any business in any industry can get started and benefit from it.
2. Online publishing curtails production and marketing costs, extends your reach into new markets, and ultimately drives more sales and conversions.
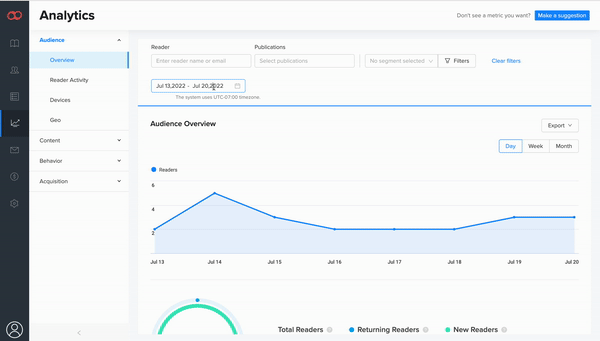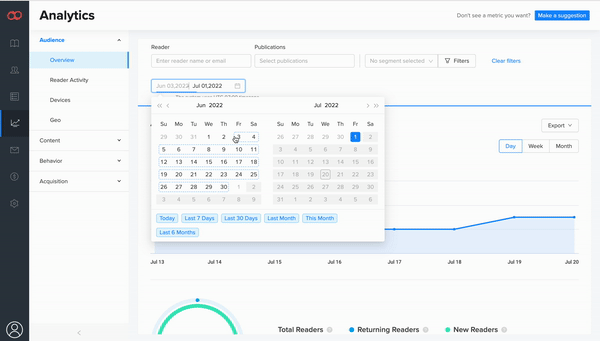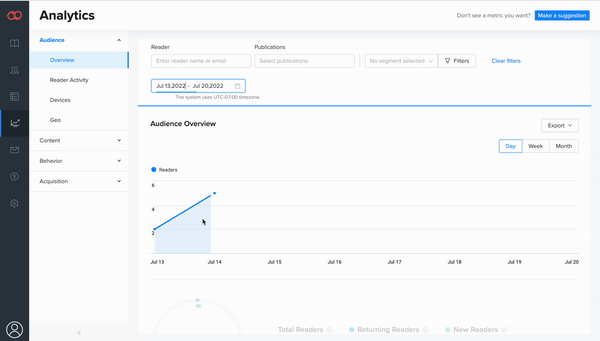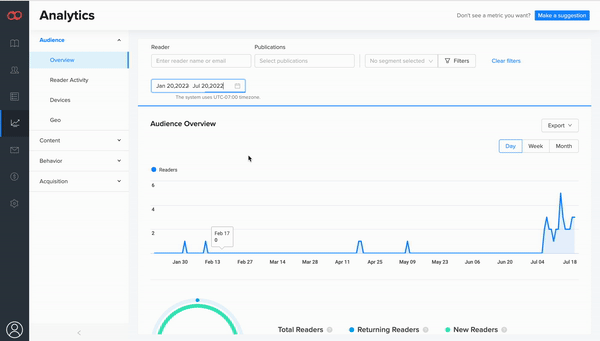
3. Performance analytics can offer an incredibly detailed view of how readers interact with your content—helping unlock its full potential in the process.
4. Digital content like online magazines and digital brochures can be distributed to the public at any time.
5. Digital publishers can easily update content in real-time, even after it’s published. Typos or outdated information can be fixed in seconds.
6. Are you a control freak? Great, because digital publishing gives you complete power over your content. Everything’s on your terms.
7. There’s a higher chance of online content going viral, and fast. People view your content → they like it → they share it on social media and other digital channels.
8. Web content is engaging and interactive. Media such as videos and photos can be embedded in online catalogs, for example, to provide a hassle-free shopping experience. You can get really creative with it.
Digital publishing cons
1. While online publishing is accessible, the learning curve can be steep for those who are entirely new to the field. Digital publishers must familiarize themselves with writing, marketing, and distribution best practices. It’s a daunting task for newcomers, but all-in-one digital publishing platforms can help offload the work.
2. Digital publishers are still shrugging off the stigma of self-publishing. For print-only veterans in the industry, having your work published by any of the “Big Five” is the only way to legitimize it. It’s an archaic way of thinking that’s (thankfully) changing.
3. Digital content is liable to technical issues and constraints, such as poor internet connections. Moreover, some readers may find it difficult to read content on smaller mobile devices.
Examples of digital publishing
1. Digital Magazines
Online magazines replicate the aesthetic and tactile experience of their print counterparts while being accessible through websites, apps, and e-readers. Digital publishing platforms like Joomag host publications such as National Geographic’s Expeditions magazine, offering readers the sensation of flipping through a glossy magazine with double-page layouts. To keep layouts polished and visuals consistent, many teams use magazine photo editing to retouch images, balance color across spreads, and optimize assets for fast loading. Expeditions magazine maintains a clean design by limiting interactive elements, typically embedding only a single hyperlink on most pages.
2. Online Newsletters
Digital newsletters deliver curated content directly to subscribers' inboxes, allowing for personalized updates, news, and special offers. They serve as a direct line of communication between publishers and their audience, fostering engagement and loyalty. These newsletters can range from simple text-based formats to rich HTML designs incorporating images and links.
3. Digital Catalogs
Digital catalogs transform traditional product listings into interactive and engaging online shopping experiences. They enable businesses to showcase their products with dynamic imagery, embedded videos, and direct purchase links, making it easier for customers to browse and buy.
4. Digital Brochures
These are interactive publications designed to promote products, services, or events. Unlike static PDFs, digital brochures offer engaging features such as animations, clickable links, and embedded multimedia, enhancing the viewer's experience and providing comprehensive information in an engaging format.
5. Presentations
Digital presentations have evolved beyond static slides to incorporate interactive elements like embedded videos, real-time polls, and clickable navigation. These enhancements make digital presentations a powerful tool for storytelling and information sharing, whether for educational purposes, business pitches, or online conferences.
5. Online Newspapers
These publications bring the traditional newspaper experience to digital platforms, updating readers with the latest news, editorials, and features. Online newspapers benefit from real-time updates, multimedia content, and interactive features like comment sections, broadening the scope of journalistic engagement.
6. Blogs
Blogs offer a platform for individuals and organizations to publish regular articles, opinion pieces, and updates. They provide a space for written content that ranges from personal narratives to professional insights, often allowing for reader interaction through comments and social sharing.
7. eBooks
Digital books that can be read on e-readers, tablets, and computers. eBooks offer features such as adjustable text sizes, embedded hyperlinks, and interactive content, making reading a more customizable and interactive experience.
8. PDFs
Portable Document Format (PDF) files are a common method for distributing fixed-layout documents digitally. While they don't offer much interactivity, PDFs are widely used for documents that require precise formatting, such as official forms and reports.
9. Mobile Apps
Applications designed for smartphones and tablets can provide unique digital publishing experiences, offering interactive content, push notifications for updates, and personalized user experiences based on data and preferences.
10. Interactive Reports
Digital reports, such as annual reports or research findings, leverage digital platforms to present data and analysis through interactive charts, videos, and clickable elements, making the information more accessible and engaging.
11. Digital Guides
Digital employee guides and handbooks serve as essential resources for onboarding and ongoing reference within organizations. These digital documents streamline the dissemination of company policies, procedures, and culture to employees, offering an interactive and easily updatable format. Unlike their printed counterparts, digital guides can include links to internal resources, embedded training videos, and interactive content such as quizzes to ensure understanding and engagement. This format not only enhances accessibility and comprehension but also allows for real-time updates, ensuring that all employees have access to the most current information.
The list goes on and on, which is unsurprising because digital publishing has crept into our daily lives. Using a search engine to find the information you need, for example, is much more practical than spending hours ransacking a library. And many distinguished universities from around the world are now offering their course materials online.
Joomag: The Trusted Digital Publishing and Content Performance Solution
Did you know that Joomag originally started as a digital publishing-only platform back in 2009? We’ve blossomed since then, and now we’re proud to say that we offer a lot more.
While we still give our customers the creative freedom to make whatever they want, we also give them the data they need to make it even better. Our recent introduction of Joomag Analytics (JMA) perfectly encapsulates our renewed emphasis on meaningful feedback and data.
Small publishers and Fortune 500 companies alike depend on us for their content marketing, corporate communications, and sales enablement needs. There are no limits to our platform, and users are free to let their imaginations run wild with every piece of content they create. Anyone can create gorgeous, interactive publications, distribute them across multiple channels, engage with audiences on a deeper level, and measure content performance with Joomag.

FAQ
1. What exactly is digital publishing?
Digital publishing involves using online technology to create, distribute, and manage content through electronic devices. It merges the traditional concept of publishing with digital innovation, allowing for the creation and dissemination of magazines, books, and other materials in digital formats. This method reaches broader audiences, reduces costs, and allows for real-time updates and detailed performance analytics.
2. What are the major advantages of digital over print publishing?
Digital publishing offers several advantages over traditional print, including lower production and marketing costs, global audience reach, real-time content updates, and detailed analytics on reader engagement. It enables publishers to easily modify content, respond quickly to audience interests, and utilize interactive elements like videos and links, making the content more engaging and accessible.
3. How has digital publishing impacted industries and content creation?
Digital publishing has revolutionized how content is created, distributed, and consumed, leading to the emergence of new industries and transforming existing ones. It has made publishing accessible to a wider range of businesses and individuals, encouraging innovation and disruption. With the rise of digital platforms, content can now reach a global audience instantly, offering interactive and engaging experiences that were not possible with traditional print methods.